

Climate zones are regions of Earth that share similar weather patterns, including temperature, rainfall, and other atmospheric conditions. The Earth's climate varies widely from place to place due to factors like latitude, altitude, and proximity to water bodies. Understanding the main climate zones helps us learn about the diversity of ecosystems, the suitability for agriculture, and the types of habitats found around the world. In this article, we will explore the main climate zones, how they differ from each other, and provide examples from various regions of the world.
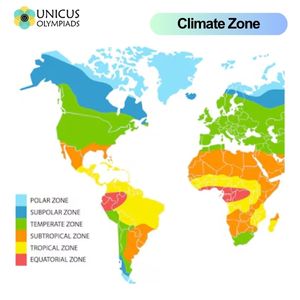
The tropical climate zone is characterized by warm temperatures year-round with little temperature variation. This climate zone is located near the Equator and is known for its consistent rainfall and high humidity levels, making it an ideal environment for lush vegetation and diverse ecosystems.
The arid climate zone, also known as the desert climate, is characterized by very low rainfall, high temperatures during the day, and large temperature fluctuations between day and night. This climate is found in regions with limited water resources and often has vast dry landscapes.
The temperate climate zone experiences moderate temperatures and distinct seasonal changes. These regions have four seasons: spring, summer, autumn, and winter, with balanced temperatures and moderate precipitation throughout the year.
The polar climate zone is found in regions near the North and South Poles, where temperatures are extremely low, and the weather is harsh. These regions have long, cold winters and short, cool summers, and they receive little precipitation, mostly in the form of snow.