

Geographical lines like the Equator and Prime Meridian play an essential role in how we locate positions on Earth and divide the world into different hemispheres. These lines form the basis of the global coordinate system, which allows us to determine the exact position of any place on the planet using latitude and longitude. In this article, we will explore how these lines divide Earth and the different types of latitudes that help us pinpoint specific locations, along with examples of their significance.
The Equator is an imaginary line that divides Earth into two equal halves: the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. It is located at 0 degrees latitude and is the longest line of latitude on Earth, measuring approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles). The Equator plays a significant role in climate, geography, and navigation.
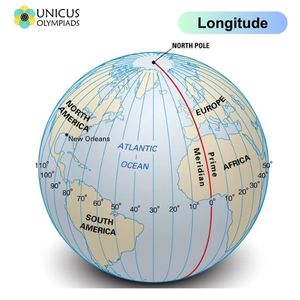
The Prime Meridian is another key geographical line, located at 0 degrees longitude. It divides Earth into the Eastern Hemisphere and the Western Hemisphere. This line runs from the North Pole to the South Pole and passes through Greenwich, England, giving it the name Greenwich Meridian. The Prime Meridian is vital for determining time zones and for global navigation.
Latitude lines are imaginary lines that run parallel to the Equator. These lines measure the distance north or south of the Equator in degrees. Latitude is crucial for determining the climate and location of a place on Earth. In addition to the Equator, several other important latitude lines divide the Earth.

Latitude and longitude are the two main coordinates used in the global coordinate system to pinpoint locations on Earth. Latitude gives the north-south position, while longitude gives the east-west position. Together, they form a grid that allows for precise location identification anywhere on Earth.