

Jet streams are fast-flowing, narrow air currents found high in the atmosphere, typically around 10 to 15 kilometers above the Earth’s surface. These powerful winds play a crucial role in shaping global weather patterns and are key components in the movement of weather systems. Jet streams affect everything from daily weather forecasts to long-term climate trends. In this article, we will explore what jet streams are, how they form, and how they influence weather patterns across the globe.
Jet streams are narrow bands of high-speed winds that blow from west to east, generally near the boundaries of different air masses. These winds can reach speeds of over 400 kilometers per hour (about 250 miles per hour) in certain areas, although typical speeds range from 100 to 200 kilometers per hour (60 to 125 miles per hour). Jet streams are found at high altitudes in the atmosphere, in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere, and they flow in relatively straight lines, although they can meander and shift depending on the season and atmospheric conditions.
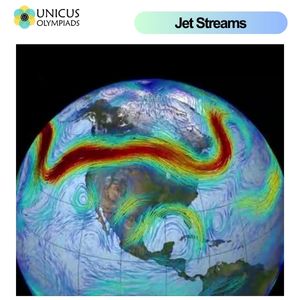
Jet streams form as a result of the Earth's rotation and the difference in temperature between the polar regions and the equator. The warm air near the equator rises and moves toward the poles, while cold air from the poles moves toward the equator. This temperature difference creates pressure differences in the atmosphere. The rotation of the Earth causes the Coriolis effect, which deflects winds to the right in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere, resulting in the west-to-east flow of air that characterizes jet streams.
Jet streams are not constant throughout the year. They tend to be stronger and more defined in the winter months, when the temperature difference between the polar and tropical regions is most pronounced. During the summer months, the jet streams weaken and shift northward, as the temperature gradient between the poles and the equator becomes less extreme.
Jet streams have a significant impact on weather patterns, as they help steer weather systems across the planet. The position and strength of a jet stream can influence everything from precipitation and temperature to the severity of storms.
Jet streams also play a key role in influencing regional climate patterns. For example, the position of the polar jet stream can affect the climate of regions in the mid-latitudes. A northward shift of the jet stream can lead to warmer, drier conditions, while a southward shift can bring cooler, wetter weather. Additionally, jet stream patterns can interact with other atmospheric phenomena, such as El Niño and La Niña, to create extreme weather events like droughts, floods, and hurricanes.
In 2014, the polar jet stream took a deep southward dive, causing an intense winter storm in the United States. This led to extremely cold temperatures, heavy snowfall, and dangerous travel conditions across many parts of the country, particularly in the Midwest and the East Coast. The jet stream's position allowed cold air from the Arctic to flow into the region, triggering the storm.
In 2018, a high-pressure ridge in the jet stream caused an extended heatwave in Europe, with temperatures reaching record highs in many countries. The jet stream remained stationary, preventing cooler air from moving in and creating prolonged hot weather that led to drought conditions and wildfires in parts of Europe.
In 2019, the polar vortex, a large area of low pressure and cold air in the stratosphere, caused the jet stream to dip drastically, leading to extreme cold weather in the United States and Canada. The jet stream's movement allowed the cold Arctic air to flow southward, bringing dangerously low temperatures to the northern parts of North America and triggering a "polar vortex" event that brought freezing temperatures, heavy snow, and icy conditions.
Scientists monitor jet streams using weather satellites, which provide real-time data on the movement of air currents at different altitudes. These satellites measure the temperature, pressure, and velocity of winds in the upper atmosphere, helping meteorologists track the position and strength of jet streams. This information is used to predict weather patterns, including the likelihood of storms, temperature shifts, and rainfall.
Numerical weather prediction models also incorporate data from jet streams to forecast weather. By analyzing the position of the jet stream and its interactions with other atmospheric systems, meteorologists can predict shifts in weather patterns. This helps to provide more accurate short-term weather forecasts and allows for advanced warnings of severe weather events.