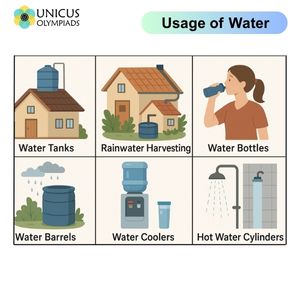
This section provides a deeper look into how water is used and stored in households. It also includes practical examples and applications to better understand the importance of water management in daily life.
Water is an essential part of daily life, and it is used for a variety of purposes. Below are some key examples and applications for water usage at home:
Storing water is essential for emergencies or when there are disruptions in the water supply. Below are examples and applications of how water is stored:
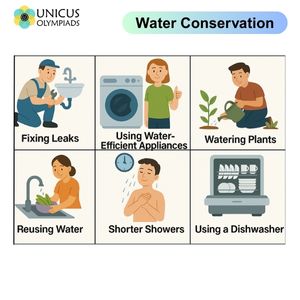
Conserving water helps save both water and money. Below are examples and applications of how water can be conserved at home: