

Earth is a dynamic and ever-changing planet. Beneath its surface, layers of rock, minerals, and molten materials interact in complex ways that drive geological processes and cause various natural events. These events, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain formation, are a result of the movement and interaction of Earth's layers and tectonic plates. In this article, we will explore how the Earth's internal structure, including its layers and tectonic plates, leads to natural events that shape the planet's surface and influence life on Earth.
The Earth is made up of several layers, each with different characteristics. These layers include the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core, and their interactions are key to understanding the causes of natural events.

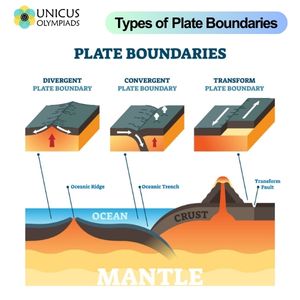
The Earth's lithosphere (the rigid outer layer) is broken into large pieces called tectonic plates. These plates float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere, a layer of the upper mantle. The movement of these plates over the Earth’s surface is a fundamental cause of geological events like earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building.
Tectonic plates move due to heat-driven processes occurring deep within the Earth. As the mantle material heats up, it rises and spreads out, causing the plates to move apart, collide, or slide past each other. This movement is driven by convection currents in the mantle and is part of the process known as plate tectonics.
Earthquakes are caused by the sudden release of energy along faults or plate boundaries. When two tectonic plates move past one another or collide, stress builds up at the fault line. When the stress exceeds the strength of the rocks, it is released in the form of seismic waves, causing the ground to shake.
Volcanoes are formed by the movement of tectonic plates at convergent and divergent boundaries. As plates move, magma from the mantle rises to the surface, causing volcanic eruptions. The release of molten rock, gas, and ash can dramatically alter landscapes and impact ecosystems.
Mountain ranges are often formed at convergent plate boundaries when two continental plates collide. The resulting compression causes the crust to fold and rise, forming mountains. Mountain-building processes, known as orogeny, are responsible for some of the tallest mountain ranges on Earth, such as the Himalayas, formed by the collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates.