

Space exploration has been one of humanity's greatest achievements, with numerous space missions pushing the boundaries of our knowledge of the universe. Two of the most iconic missions in space history are the Apollo 11 mission, which landed the first humans on the Moon, and India’s Chandrayaan missions, which aim to explore the Moon's surface and its resources. These missions, along with many others, have paved the way for further exploration of the cosmos, offering insights into planetary science, human spaceflight, and the potential for future lunar exploration. This article explores the achievements of the Apollo 11 and Chandrayaan missions, highlighting their significance and impact on space exploration.
The Apollo 11 mission, launched by NASA in 1969, marked a historic milestone in space exploration by successfully landing the first humans on the Moon. The mission's objective was to perform a crewed landing on the lunar surface and return safely to Earth. It was the culmination of NASA's Apollo program, which aimed to demonstrate U.S. technological superiority in the space race during the Cold War and to expand human knowledge of the Moon.

Apollo 11’s achievement was not only a technological triumph but also a symbolic one. It marked the first time humanity had ever ventured beyond Earth, and the mission successfully fulfilled U.S. President John F. Kennedy's promise to land a man on the Moon and return him safely to Earth before the end of the 1960s. The success of Apollo 11 solidified the U.S. as a leader in space exploration and helped expand humanity's understanding of space. The mission also demonstrated that human spaceflight could be conducted over long distances and safely return to Earth.
The Chandrayaan missions are India's lunar exploration program, launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). These missions aim to explore the Moon’s surface, understand its composition, and discover potential resources. The Chandrayaan program has contributed significantly to global lunar research, especially in terms of understanding the Moon’s water content and surface features.
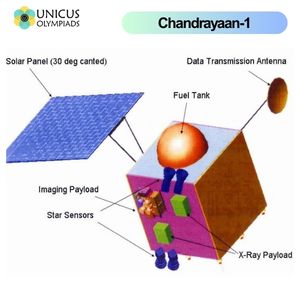
Launched on October 22, 2008, Chandrayaan-1 was India’s first mission to the Moon. The mission aimed to survey the lunar surface, map its mineral composition, and search for water ice at the lunar poles. Chandrayaan-1 carried 11 scientific instruments, including those developed by NASA and ESA, and was equipped with a moon impact probe that was released on the Moon’s surface.
Launched on July 22, 2019, Chandrayaan-2 was India’s second attempt to explore the Moon. This mission had three components: an orbiter, a lander named Vikram, and a rover called Pragyan. Chandrayaan-2’s main objective was to study the lunar south pole, a region where water ice has been detected but not yet fully explored.

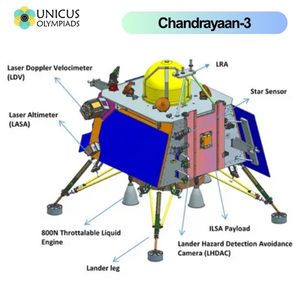
Chandrayaan-3 is India’s next mission to the Moon, scheduled for launch in 2022. Unlike its predecessors, Chandrayaan-3 will consist only of a lander and a rover, with no orbiter (since the Chandrayaan-2 orbiter is still operational). The mission's goal is to successfully land on the Moon’s surface, particularly the south pole, and deploy the rover to study the surface composition and search for signs of water and other elements.
While the Apollo 11 mission remains one of the most significant milestones in human space exploration, marking the first human landing on the Moon, the Chandrayaan missions have made important contributions to lunar science, especially in discovering water on the Moon and studying its surface composition. Apollo 11 was a landmark for human spaceflight, while the Chandrayaan missions have contributed to our understanding of the Moon, particularly in the context of future lunar exploration.
| Mission | Key Achievement | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Apollo 11 | First manned Moon landing | Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin became the first humans to walk on the Moon on July 20, 1969. Collected lunar samples, performed experiments, and returned safely to Earth. |
| Chandrayaan-1 | Discovery of water on the Moon | Confirmed the presence of water molecules on the Moon’s surface in 2009. Helped map the lunar surface and study the Moon’s mineral composition. |
| Chandrayaan-2 | Study of lunar south pole | Orbiter continues to send back data on lunar surface composition and water ice. Vikram lander’s mission faced challenges but provided important lessons for future missions. |
| Chandrayaan-3 | Planned successful landing and rover deployment | Scheduled for launch in 2022. Aims to successfully land a rover on the Moon’s surface and continue the exploration of lunar resources. |