

Trade routes have played a crucial role in connecting distant regions and facilitating the exchange of goods, cultures, and ideas. One of the most famous of these routes is the Silk Road, which spanned continents and brought together East and West for over a millennium. Trade routes such as the Silk Road, the Spice Route, and others enabled the movement of valuable goods, including silk, spices, precious metals, and textiles, but they also helped spread technology, religion, and knowledge. In this section, we will explore how these trade routes linked different regions of the world and their lasting impact on history.
The Silk Road was an ancient network of trade routes that connected China with Central Asia, the Middle East, and Europe. It is often considered one of the most important trade routes in history, facilitating the exchange of goods and culture between East and West.
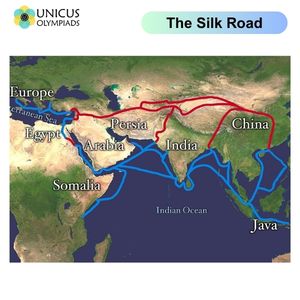
While the Silk Road is the most famous, other trade routes have also been critical in linking different regions of the world, enabling the exchange of goods, ideas, and culture.
The Spice Route refers to the sea and land routes that linked Southeast Asia, the Indian subcontinent, and the Arabian Peninsula to Europe and Africa, primarily for the trade of spices.
The Trans-Saharan trade routes linked sub-Saharan Africa with North Africa, facilitating the exchange of goods across the Sahara Desert.
The Incense Route connected southern Arabia with the Mediterranean world, enabling the trade of frankincense, myrrh, and other valuable aromatic substances.